States of Matter: Understanding the Phases of Substance
Introduction: The study of matter encompasses its various forms and behaviors, known as the States of Matter. This fundamental concept delves into the distinct phases—solid, liquid, gas, and plasma—each characterized by unique properties and responses to changes in temperature and pressure.
Solid State: In the solid state, particles are closely packed in a regular arrangement, exhibiting a fixed shape and volume. Intermolecular forces play a crucial role in determining the strength and stability of solids, influencing properties such as hardness and conductivity.
Liquid State: Liquids, with particles that have more freedom of movement than solids, take the shape of their container while maintaining a constant volume. Surface tension and viscosity define liquid behavior, reflecting the cohesive forces between molecules.
Gaseous State: In the gaseous state, particles are highly energetic and move freely, filling the entire space available to them. Gas behavior is governed by factors such as pressure, volume, and temperature, as described by the ideal gas law.
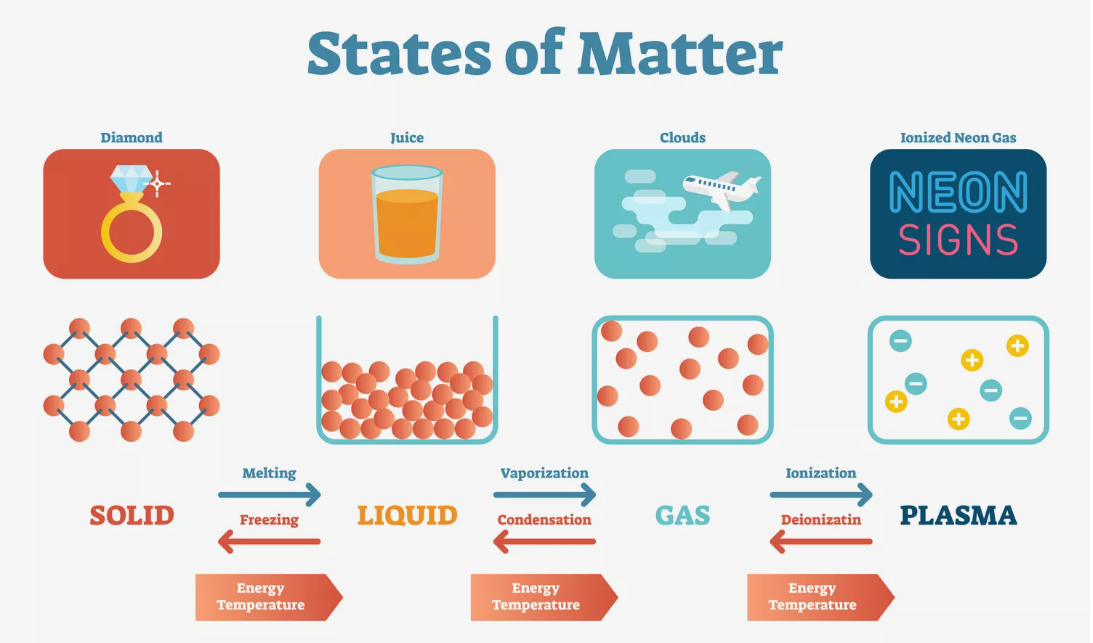
Plasma State: Less commonly encountered on Earth, plasma represents a state of matter where high energy levels strip electrons from atoms, creating a mixture of charged particles. Found in stars and certain industrial processes, plasma exhibits unique electrical and magnetic properties.
Changes of State: Transitions between states, known as phase changes, occur with alterations in temperature or pressure. Processes like melting, freezing, condensation, and vaporization highlight the dynamic nature of matter as it undergoes transformations between solid, liquid, and gas states.
Critical Point and Phase Diagrams: Understanding the critical point, the conditions at which distinct phases merge, is crucial. Phase diagrams illustrate the relationships between temperature, pressure, and states of matter, providing a visual representation of the boundaries between phases.
| Topic Name | |
|---|---|
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
Class 11 |
Download |
